CFD Trading
Learn CFD Trading with Eonefx
Eonefx provides an easy-to-use platform for CFD trading, designed for both beginners and experienced traders in Dubai and the UAE. By following the correct steps and managing risks wisely, you can make the most of your trading potential.
4 Steps to Trading CFDs
1: Learn What CFD Trading Is
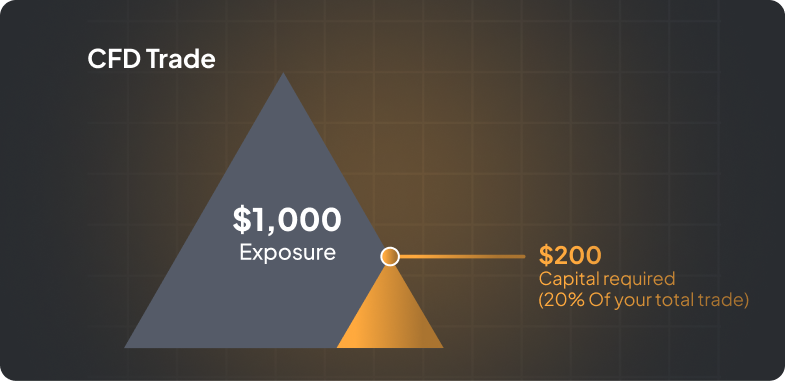
Before getting started, it’s essential to understand the basics of CFD trading. CFDs, or *Contracts for Difference*, let you trade on the price movements of assets like stocks, forex, commodities, and indices. Unlike traditional investments, CFD trading uses leverage, so a smaller deposit can control a larger trade, but it also increases risk. Familiarize yourself with how leverage works and the risks involved.
2: Fill in a Simple Form
To begin, create an account with Eonefx by completing a quick online registration form. This is the first step toward accessing the markets.
3: Get Verified
Submit identification documents to verify your account and meet regulatory requirements. Verification helps secure your account and allows you to start trading.
4: Fund and Start Trading
Once verified, deposit funds into your account to begin placing your first trades. You’re now ready to start trading in the global markets.
- Registration: Visit the broker’s website and click on the option to open a new account. You’ll need to provide personal information, including your name, address, date of birth, and contact details.
- Verification: Most brokers require you to verify your identity and address before you can start trading. This process usually involves submitting copies of identification documents (such as a passport or driver’s license) and a utility bill or bank statement as proof of address.
- Account Type: Choose the type of account that suits your trading style. Brokers often offer different account types, such as standard accounts, mini accounts, and ECN accounts. The type of account you choose will determine factors like the minimum deposit, leverage, and spread structure.
- Fund Your Account: Once your account is verified, you’ll need to deposit funds to start trading. Brokers offer various payment methods, including bank transfers, credit/debit cards, and e-wallets like PayPal or Skrill. Start with an amount you’re comfortable with, especially if you’re new to trading.
Choose Your Market and Timeframe
CFDs let you trade various markets, including forex, commodities, and indices. Choose a market you’re comfortable with and select a trading timeframe that matches your goals:
- Short-term trading is ideal for quick price movements.
- Long-term trading suits those looking to hold positions for extended periods.
Your strategy will vary depending on your market choice and timeframe, so it’s essential to plan accordingly.
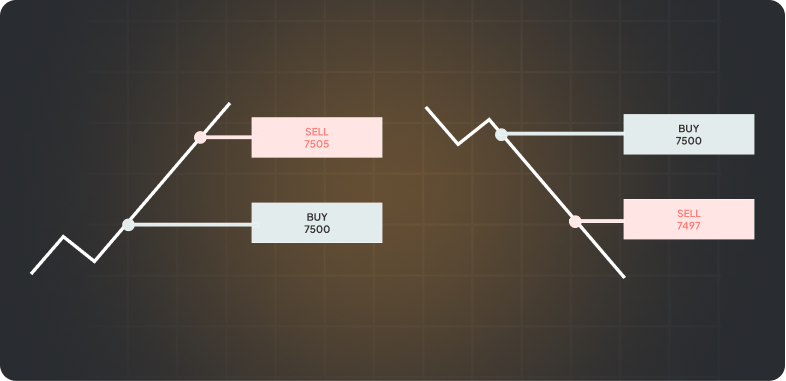
Decide Whether to Buy or Sell
CFD trading offers flexibility to profit from both market directions:
- Buy (Go Long): If you expect the asset price to rise, you open a buy position to profit from the upward movement.
- Sell (Go Short): If you believe the price will fall, you open a sell position, allowing you to benefit from the price drop.
This flexibility makes CFDs popular among traders looking to make the most of both market ups and downs.

Set Your Stops and Limits
Using stop-loss and limit orders helps manage your risk and protect your profits:
- Stop-Loss Order: Automatically closes your position if the market moves against you, minimizing losses.
- Limit Order: Closes your trade at a specific profit target when the market reaches your desired level.
Setting stops and limits helps you stay in control of your trades, even if the market changes suddenly.
Monitor Your CFD Trade and Close Your Position
After placing your trade, monitor the market to stay informed about price changes. Eonefx provides advanced tools to help you adjust your stops and limits as needed. When your profit target is reached or if the market changes direction, close your position to lock in gains or minimize losses.
CFD Trading Examples
Here are practical examples of how CFD trading works:
- Example 1: You buy a CFD on an index at 3000 points. The index rises to 3050 points, resulting in a profit.
- Example 2: You short-sell a commodity CFD at $100. The price drops to $95, earning you a gain.
These examples show how CFD trading allows you to benefit from both upward and downward price movements.
Conclusion
CFD trading provides flexibility, with the potential for profit and the ability to trade a wide range of markets. However, it also involves risks due to leverage and market volatility.
By choosing your markets carefully, setting stops and limits, and monitoring your trades, you can create a more controlled and rewarding trading experience. Start trading CFDs with Eonefx today and explore new market opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Costs vary depending on the broker and the asset you trade but typically include:
- Spreads: The difference between the buy and sell price.
- Commissions: Some brokers charge commissions, especially on share CFDs.
- Overnight Financing (Swap): A fee applied for holding positions overnight, based on the interest rate difference between the two currencies in a currency pair or other applicable rates for other assets.
Understanding these costs helps you manage your trading expenses and set realistic profit targets.
Risk management is crucial in CFD trading, especially with leverage involved. You can manage risk by:
- Setting stop-loss orders to automatically close trades that reach a specific loss level.
- Using limit orders to lock in profits once a target price is reached.
- Adjusting position sizes and leverage according to your risk tolerance.
Understanding and utilizing these tools helps protect your capital and manage potential losses.
While both CFDs and futures contracts allow you to speculate on the price movement of assets, they differ in some key ways:
- Ownership: CFDs don’t involve owning the underlying asset, while futures are contracts to buy or sell the asset at a future date.
- Expiration: CFDs don’t usually have expiration dates, so you can hold positions as long as the market is open, while futures contracts have specific expiration dates.
- Flexibility: CFDs are generally more flexible, with lower contract sizes and the ability to go long or short with ease.